Vitamin B12 is one of the most essential nutrients for the human body. It plays a key role in making red blood cells, supporting the nervous system, and keeping our energy levels stable. Yet, many people around the world suffer from vitamin B12 deficiency without even realizing it. The symptoms can be subtle at first, but if ignored, they may lead to serious health problems.
The causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies for vitamin B12 deficiency.
What is Vitamin B12?
- Vitamin B12, also called cobalamin, is a water‑soluble vitamin.
- It helps in the production of DNA and red blood cells.
- It supports the brain and nervous system.
- Unlike other vitamins, B12 is mainly found in animal‑based foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
Why is Vitamin B12 Important?
- Energy production: It helps convert food into energy.
- Healthy blood: Prevents anaemia by supporting red blood cell formation.
- Nervous system: Maintains nerve health and communication between brain and body.
- Mental health: Supports memory, focus, and mood regulation.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:-
Early Signs
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Dizziness or breathlessness
- Tingling in hands and feet (pins and needles)
- Loss of appetite
Advanced Symptoms
- Numbness in toes or fingers
- Difficulty walking or balancing
- Memory problems and confusion
- Mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- Vision disturbances
Many of these symptoms are linked to nerve damage. If deficiency continues for a long time, the damage can become permanent.
Who is at Risk?
Certain groups of people are more likely to develop vitamin B12 deficiency:
- Vegans and vegetarians: Since B12 is found mostly in animal products, plant‑based diets often lack it.
- Older adults: With age, the stomach produces less acid, reducing absorption.
- People with digestive disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, coeliac disease, or IBS affect absorption.
- Patients with stomach or intestinal surgery: Removal of parts of the digestive tract reduces B12 absorption.
- Medication users: Long‑term use of acid‑reducing drugs or metformin can lower B12 levels.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Increased nutritional demand can lead to deficiency if diet is not balanced.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:-
- Poor diet: Lack of animal‑based foods.
- Pernicious anaemia: An autoimmune condition that prevents absorption.
- Alcohol dependence: Alcohol interferes with nutrient absorption.
- Low stomach acid: Needed to release B12 from food.
- Genetic factors: Some people naturally absorb less B12.
How is Deficiency Diagnosed?
- Blood tests: Measure B12 levels.
- Complete blood count (CBC): Detects anaemia.
- Homocysteine and methylmalonic acid tests: High levels indicate deficiency.
- Physical examination: Doctors check for neurological symptoms.
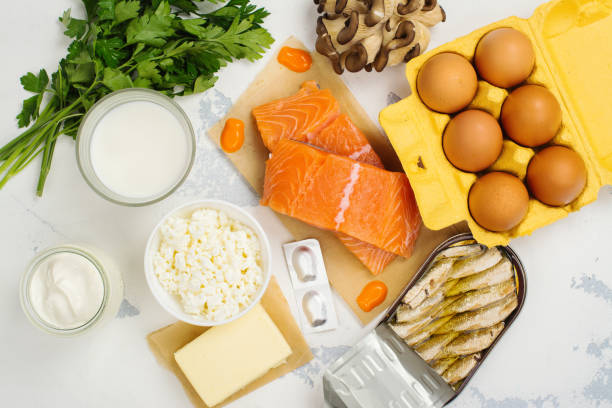

Treatment Options:-
- Dietary changes: Include more meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Supplements: Oral tablets or capsules.
- Injections: For severe deficiency, doctors prescribe B12 injections.
- Fortified foods: Plant‑based milk, cereals, and nutritional yeast often contain added B12.
Long‑Term Effects if Ignored:-
- Permanent nerve damage
- Severe anaemia
- Memory loss and dementia‑like symptoms
- Heart problems due to high homocysteine levels
- Reduced quality of life
Posted onEdit”Your Heart Could Be Warning You at Night:-“
Prevention Tips:-
- Eat a balanced diet with B12‑rich foods.
- Vegans should take supplements or fortified foods.
- Get regular health check‑ups, especially if you are in a high‑risk group.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Discuss with your doctor if you are on long‑term medication.

Real‑Life Example:-
Imagine a young professional who feels tired all the time. She blames her busy schedule, but later discovers she has vitamin B12 deficiency. With supplements and diet changes, her energy returns, and her concentration improves. This shows how important it is to listen to your body’s signals.
Quick Checklist
- Constant fatigue?
- Tingling in toes or fingers?
- Pale skin or dizziness?
- Memory lapses or mood swings?
If yes, consult a doctor and check your B12 levels.
Conclusion:-
Vitamin B12 deficiency is common but often overlooked. The symptoms may start small, like tiredness or tingling in the toes, but they can grow into serious health issues if ignored. The good news is that deficiency is preventable and treatable. With a balanced diet, supplements when needed, and regular check‑ups, you can protect your health and energy.
MORE INFORM:- newmobilephoneunder25k.de



